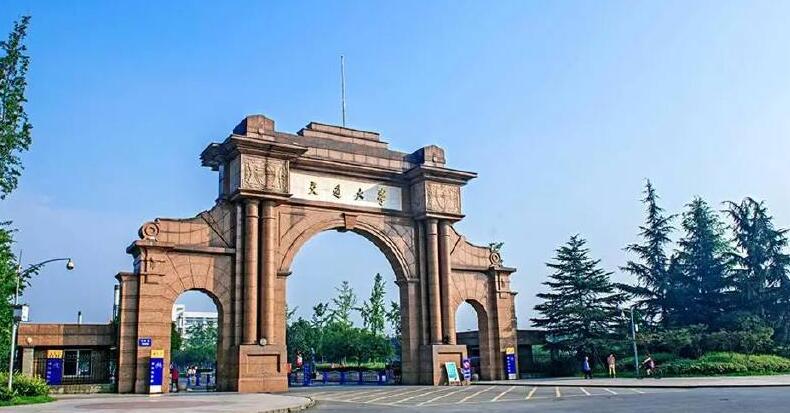

 Southwest Jiaotong University was founded in 1896. It is one of the
earliest universities in the modern history of China. It is also the cradle
of higher education in Civil Engineering, Traffic Engineering, Mining and
Metallurgical Engineering in China. After several historic moves, it is
presently located in Chengdu, the capital city of Sichuan province in China.
With more than two century efforts, SWJTU has made great progress and taken
a leading role in the railway transport techniques over the world. In 2017,
SWJTU has been selected by Chinese government as the first batch of world-class
university and world-class subject construction project. In recent years,
SWJTU aims at promoting the development in Science, in addition to the
advance in Technology. Meanwhile, the School of Physical Science and Technology
of SWJTU has become an integrated teaching-research college. In accordance
with the national energy development strategy, SWJTU has been devoted to
the area of magnetic confinement fusion research and the Institute of Fusion
Science in the School is actively working on theoretical simulations and
experimental studies over a wide range of fusion research subjects.
Southwest Jiaotong University was founded in 1896. It is one of the
earliest universities in the modern history of China. It is also the cradle
of higher education in Civil Engineering, Traffic Engineering, Mining and
Metallurgical Engineering in China. After several historic moves, it is
presently located in Chengdu, the capital city of Sichuan province in China.
With more than two century efforts, SWJTU has made great progress and taken
a leading role in the railway transport techniques over the world. In 2017,
SWJTU has been selected by Chinese government as the first batch of world-class
university and world-class subject construction project. In recent years,
SWJTU aims at promoting the development in Science, in addition to the
advance in Technology. Meanwhile, the School of Physical Science and Technology
of SWJTU has become an integrated teaching-research college. In accordance
with the national energy development strategy, SWJTU has been devoted to
the area of magnetic confinement fusion research and the Institute of Fusion
Science in the School is actively working on theoretical simulations and
experimental studies over a wide range of fusion research subjects.
To further promote the magnetic fusion research activities at SWJTU, the university leadership decided to pursuit stellarator physics since its unique configuration is of significance for fusion science, while at present the major line of fusion development in China is the tokamak configuration only! Such a comprehensive understanding is strongly supported by top-level fusion scientists in China. At the beginning in year 2015, for learning and gaining research experience in stellarator devices, SWJTU intended to transfer the CHS device from the National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS) in Japan. Later on, after further discussions with NIFS side, SWJTU decided to jointly construct a new stellarator with NIFS together with an advanced configuration design. It is named as “Chinese First Quasi-axisymmetric Stellarator (CFQS)”. In July 2017, SWJTU and NIFS signed a MoU, where the roles of both sides were specified. SWJTU is responsible for the construction of the CFQS and experimental facilities, jointly designing the device and executing experiments with NIFS and other international researchers. NIFS is leading the design work and associated research programs, contributing to heating equipment and diagnostics of the experiments.
 Chengdu is the capital city of China’s southwest Sichuan province. The
city is located in the west of Sichuan Basin and in the center of Chengdu Plain. It is famed for being the home of cute giant pandas.
The city covers about a total area of 14.3 thousand square kilometers with
a population of over 16 million. Because of the advantageous Dujiangyan
irrigation system constructed in 256 B.C., it has rich natural resources
and mild climate, and hence, is reputed as Heavenly State (Tian Fu Zhi
Guo 天府之國 in Chinese). While the economy of Chengdu city is rapidly growing up,
people in the city have strong interest in the development of cultural
and scientific activities. In recent years, Chengdu is planning to build
a new academic zone (park) to expedite the development in science and technology.
The CFQS project of SWJTU has been selected as one of main scientific programs
there. As the transport hub in southwest of China, Chengdu is easily approached
by both air routes and railways. The city bus and metro continue to develop,
providing the locals and the tourists with great convenience. Domestic
and oversea fusion and stellarator researchers are warmly welcomed to visit
Chengdu and also to join the CFQS experiments in the near future.
Chengdu is the capital city of China’s southwest Sichuan province. The
city is located in the west of Sichuan Basin and in the center of Chengdu Plain. It is famed for being the home of cute giant pandas.
The city covers about a total area of 14.3 thousand square kilometers with
a population of over 16 million. Because of the advantageous Dujiangyan
irrigation system constructed in 256 B.C., it has rich natural resources
and mild climate, and hence, is reputed as Heavenly State (Tian Fu Zhi
Guo 天府之國 in Chinese). While the economy of Chengdu city is rapidly growing up,
people in the city have strong interest in the development of cultural
and scientific activities. In recent years, Chengdu is planning to build
a new academic zone (park) to expedite the development in science and technology.
The CFQS project of SWJTU has been selected as one of main scientific programs
there. As the transport hub in southwest of China, Chengdu is easily approached
by both air routes and railways. The city bus and metro continue to develop,
providing the locals and the tourists with great convenience. Domestic
and oversea fusion and stellarator researchers are warmly welcomed to visit
Chengdu and also to join the CFQS experiments in the near future.